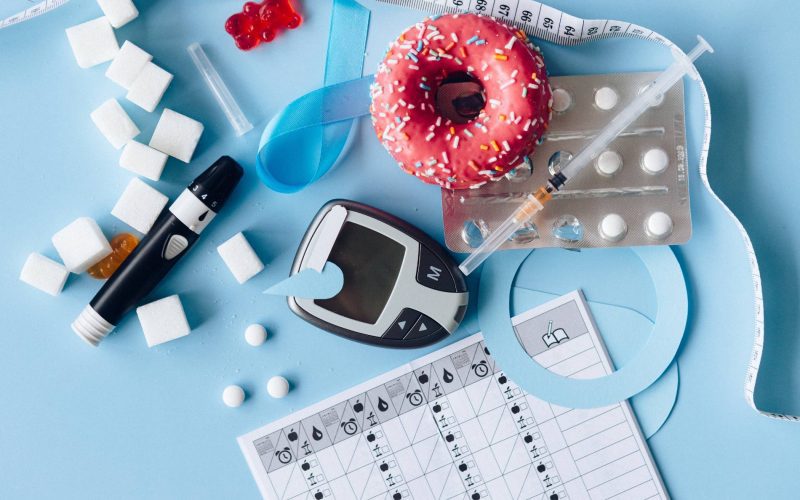
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that significantly impacts the regulation of glucose in the body, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia. Individuals with diabetes also experience increased sugar content in their urine. This chronic condition arises from the body’s inability to produce adequate amounts of insulin or utilize it effectively. In this article, we delve into the types of diabetes, the underlying causes, and the importance of proper management for overall well-being.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus encompasses several distinct types, each with its own characteristics and management approaches. Understanding these types is essential for effectively addressing the condition.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, typically develops in childhood or adolescence. In this form of diabetes, the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin due to the destruction of insulin-secreting cells. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes, the most common type of diabetes, generally occurs in adulthood, although it can manifest at any age. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production. While genetic factors play a role, lifestyle choices, such as poor diet and sedentary behavior, contribute significantly to its development. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed through lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and, in some cases, oral medications or insulin therapy.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects women who did not previously have diabetes. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Although gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, affected women have a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Managing blood sugar levels through proper diet, regular exercise, and, in some cases, medication is crucial to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Managing Diabetes Mellitus
Efficient management of diabetes mellitus is vital for minimizing the risk of complications and promoting overall well-being. Here are some key aspects of diabetes management:
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels throughout the day. This information enables them to make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication intake. Blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals to maintain optimal control over their condition.
Healthy Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is paramount for individuals with diabetes. A well-balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or aerobic exercises, enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes overall health. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are essential for effective diabetes management.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage diabetes. Oral medications, such as metformin, and other antidiabetic drugs can be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes or advanced Type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to ensure proper glucose control.
Taking Charge of Diabetes Mellitus
Understanding the different types of diabetes and the significance of proper management empowers individuals to lead fulfilling lives despite their condition. Regular medical check-ups, adherence to prescribed treatment plans, and ongoing education about diabetes are key elements in effectively managing this chronic disease.