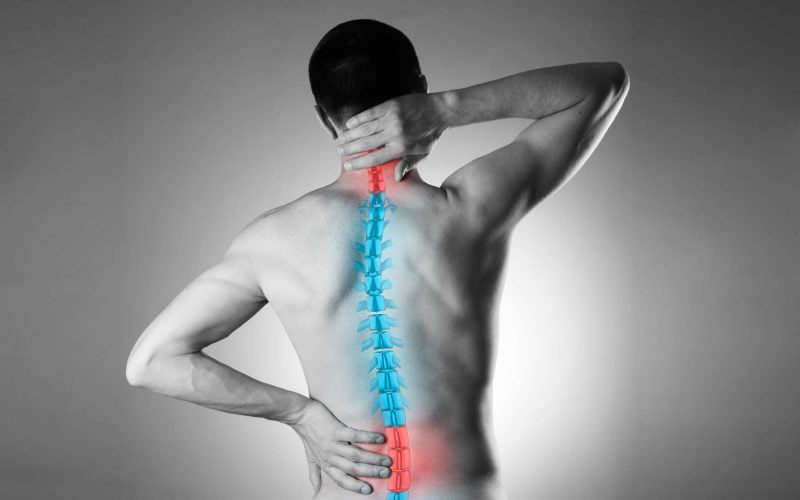
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain and discomfort caused by the compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the body, originating from the lower back and extending down the back of each leg. It provides sensation to the back of the thigh, calf, foot, and toes, as well as controls the movement of muscles in the lower leg and knee. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sciatica.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica can be caused by various factors, including:
- Herniated Disc: A herniated or slipped disc occurs when the soft cushion-like material between the vertebrae in the spine ruptures or bulges, putting pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress the sciatic nerve.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs between our vertebrae naturally degenerate, which can lead to the compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Piriformis Syndrome: The piriformis muscle, located in the buttocks, can sometimes tighten or spasm, irritating the sciatic nerve.
- Trauma or Injury: Accidents or injuries that directly impact the lower back or pelvic region can result in sciatic nerve compression.
Symptoms of Sciatica
The most common symptom of sciatica is pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve. However, the specific symptoms can vary from person to person. Some common signs of sciatica include:
- Sharp or shooting pain in the lower back that extends down the leg.
- Numbness or tingling sensation in the back of the thigh, calf, foot, or toes.
- Weakness in the affected leg or difficulty in moving the leg or foot.
- Burning or electric shock-like sensations.
It’s important to note that sciatica typically affects only one side of the body, and the symptoms may worsen with prolonged sitting, standing, or movement.
Diagnosing Sciatica
If you suspect you have sciatica, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. During the diagnostic process, the doctor will evaluate your medical history, perform a physical examination, and may recommend diagnostic tests such as:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans can help identify the underlying cause of sciatica, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of your muscles and nerves to determine if there is any nerve damage associated with sciatica.
Treatment Options for Sciatica
The treatment for sciatica depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription medications or muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles that support the spine and improve flexibility. They may also incorporate techniques such as hot or cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation around the affected nerve.
- Surgery: In rare cases where conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgery aims to remove the source of compression on the sciatic nerve, such as a herniated disc or bone spur.
It is important to note that the treatment approach for sciatica should be tailored to the individual, and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Remember, if you are experiencing symptoms of sciatica, seeking medical advice and following appropriate treatment can help alleviate pain, restore mobility, and enhance your overall well-being.