Introduction
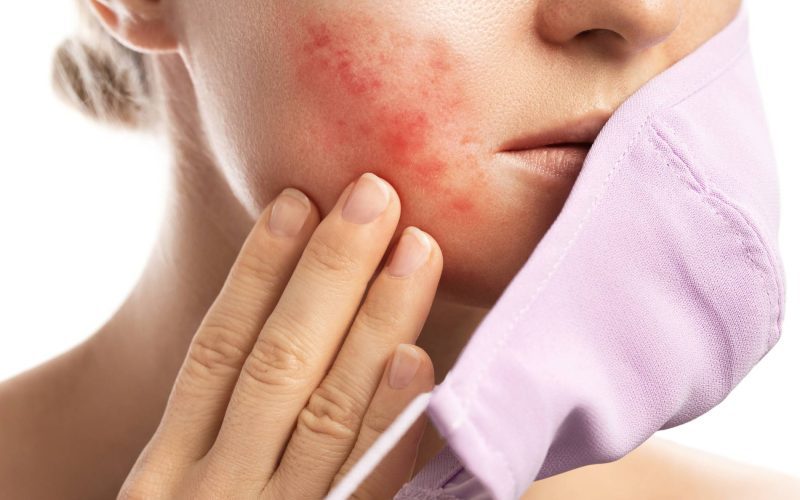
Rosacea is a recurring skin condition characterized by inflammation or patchy flushing in the central areas of the face, including the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. While it primarily affects these areas, it can also impact the neck, chest, ears, and scalp. Although rosacea is generally considered a harmless condition, it can cause irritation and a burning sensation in the eyes if it affects the ocular region. The severity of rosacea can vary, and the condition does not necessarily worsen over time.
Demographics
Rosacea is more commonly observed in Caucasians and individuals with fair complexions. It has often been referred to as the “curse of the Celts,” but it can also affect people of various ethnicities and skin types. While both sexes can develop rosacea, it tends to be more prevalent in women. The condition typically manifests between the ages of 30 and 50, often leading to misdiagnosis as sunburn or adult acne.
Symptoms
The key symptoms of rosacea include:
- Burning and stinging sensations in the face.
- Facial flushing or reddening unrelated to sweating, resulting in persistent redness.
- Inflamed papules and pustules without whiteheads or blackheads.
- Cool cheeks that do not warm up.
- Dilated blood vessels visible as red lines on the face (telangiectasia).
- In advanced cases, primarily seen in men, thickening of the skin on the nose, leading to a bulbous appearance known as rhinophyma.
- Eye involvement, which can cause pinkeye (conjunctivitis), inflamed eyelids (blepharitis), dry and gritty eyes, and recurrent sties.
Causes
The exact causes of rosacea are not fully understood, but several theories exist:
- Blood disorders: Some researchers suggest that rosacea may be triggered by underlying blood disorders that cause inflammation, leading to facial redness.
- Genetic predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that certain individuals have a genetic predisposition to rosacea. Environmental factors may then trigger the condition in these individuals.
- Skin mites: It has been observed that the presence of skin mites, specifically Demodex folliculorum, living in facial hair follicles can contribute to the development of rosacea. These mites may clog the sebaceous gland openings and cause inflammation.
Treatment Options
The treatment for rosacea varies depending on the severity of the condition. Individuals with mild to moderate rosacea can employ self-help methods and make lifestyle adjustments to manage their symptoms. These may include:
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding factors that exacerbate the condition, such as spicy foods, alcohol, extreme temperatures, and certain skincare products.
- Daily skincare routine: Establishing a gentle skincare regimen using non-irritating products specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
- Cosmetics: Utilizing cosmetics that are non-comedogenic and designed for sensitive skin to mask redness and improve the appearance of the skin.
In more severe cases, medical intervention may be necessary. Treatment options for moderate to severe rosacea include:
- Topical therapy: The application of prescription creams or gels containing antibiotics, retinoids, or other anti-inflammatory agents to reduce inflammation and control symptoms.
- Oral therapy: In some cases, oral medications, such as antibiotics or isotretinoin, may be prescribed to target inflammation and minimize the occurrence of flare-ups.
- Laser and light-based therapies: These procedures, performed by dermatologists, utilize specific wavelengths of light to target blood vessels and reduce redness and visible blood vessels associated with rosacea.
Remember, if you suspect that you have rosacea, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. With proper management and care, you can effectively control your symptoms and minimize the impact of rosacea on your daily life.